Cognitive Abilities and Lifestyle Choices: Exploring the Connection
Mar 11, 2025 / zsfcdn103/
The Role of Diet in Cognitive Function
Understanding Nutritional Neuroscience
Nutritional neuroscience is a rapidly growing field that examines how our dietary choices impact brain health and cognitive performance. Research shows that nutrients in our diet significantly influence brain function, shaping everything from memory to decision-making. Studies indicate that essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals are crucial for maintaining cognitive prowess and preventing cognitive decline.
For instance, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, are linked to improved memory and mood regulation. These fatty acids are pivotal for building cell membranes in the brain and promoting communication between neurons. Likewise, antioxidants, which are abundant in fruits and vegetables, play a vital role in reducing oxidative stress, a key contributor to neurodegenerative diseases.
Moreover, the gut-brain connection emphasizes the importance of gut health in cognitive function. A diet rich in fiber and probiotics supports a healthy microbiome, which has been shown to disproportionately affect cognitive abilities and emotional well-being. This emerging link further reinforces the idea that what we eat can profoundly influence our mental capabilities.
The Impact of Sugar and Processed Foods on the Brain
Excessive sugar intake and the consumption of processed foods have been correlated with negative effects on cognitive health. These types of foods can lead to inflammation and insulin resistance, which, in turn, disrupt brain function and can impair cognitive abilities over time. Therefore, monitoring and limiting processed food consumption is essential for maintaining optimal brain health.
Studies show that diets high in sugar can lead to a decline in memory influence and cognitive flexibility, illustrating the potential dangers of sweets. Whole, unprocessed foods tend to provide balanced nutrients that support the structural and functional integrity of the brain. A high-sugar diet may contribute not only to weight gain but also to cognitive deterioration.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to note that adopting a balanced diet consisting of whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables can mitigate these risks. Avoiding refined sugars and processed snacks encourages better mood stabilization and cognitive performance, positively impacting individuals' work and daily activities.
Dietary Interventions for Cognitive Enhancement
Implementing specific dietary interventions can significantly enhance cognitive functions. For example, the Mediterranean diet, rich in whole grains, nuts, fish, and healthy oils, is associated with improved cognitive longevity and reduced risk of dementia. This diet emphasizes diversity and nutrient density, promoting brain health through the consumption of various beneficial foods.
Another dietary approach that has garnered attention is the MIND diet, which combines elements of the Mediterranean and DASH diets specifically targeting brain health. This diet encourages the consumption of leafy greens, berries, nuts, and olive oil, all linked to improved cognitive function and a lower risk of neurodegenerative conditions.
To further support cognitive enhancements, hydration should not be neglected. Adequate water intake plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal cognitive performance. Dehydration has been linked to cognitive impairments such as reduced attention and memory difficulties. Therefore, incorporating hydration strategies into daily routines can further bolster cognitive functioning.
Physical Activity: Fuel for the Brain
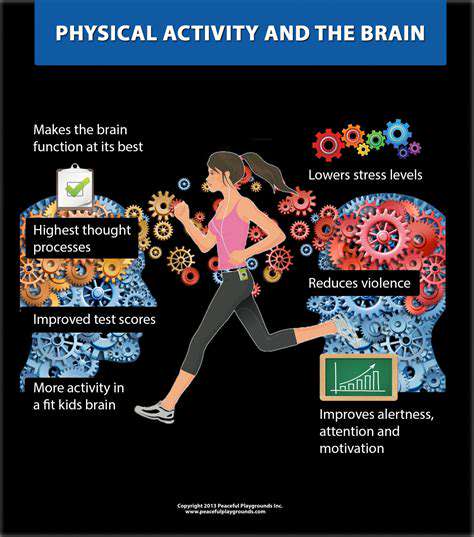
Understanding the Connection Between Physical Activity and Brain Function
Physical activity is not just essential for physical health; it plays a crucial role in enhancing brain function and cognitive abilities. Engaging in regular exercise promotes better blood flow to the brain, which is vital for optimal performance. Research indicates that people who actively engage in physical activities have improved memory, problem-solving skills, and attention spans, making them better equipped to handle daily challenges. Consequently, incorporating physical activity into one’s routine can significantly boost overall brain health.
Moreover, different types of physical activities yield various benefits for cognitive functioning. Aerobic exercises, such as running or swimming, have been linked to increased neurogenesis, which is the process of forming new neurons. This aspect of brain development is particularly important as it helps in maintaining a healthy and agile mind throughout life. In contrast, activities requiring coordination and balance, like dance or martial arts, have shown to enhance cognitive flexibility, allowing individuals to adapt and respond to changing circumstances more effectively.
As important as the activities themselves are the psychological benefits that come with physical exercise. Regular physical activity can alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, leading to improved mood and cognitive function. An uplifted mood, in turn, enhances one’s ability to focus and think critically. This emotional and cognitive synergy is what makes exercise a comprehensive tool for boosting brain power.
Finally, the social aspect of physical activity cannot be overlooked. Participating in group exercises or team sports fosters social connections, which are integral to mental health. Engaging with others during physical activities encourages camaraderie and can lead to the development of supportive relationships. These connections contribute to better cognitive outcomes and create a well-rounded approach to maintaining a healthy brain.
Recommendations for Integrating Physical Activity into Daily Life
To effectively harness the cognitive benefits of physical activity, it is essential to develop a structured routine that incorporates various forms of exercise. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, which can easily fit into a busy schedule. Simple modifications, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or going for brisk walks during lunch breaks, can significantly elevate heart rates and boost cognitive flexibility. Even small shifts in behavior can lead to substantial improvements in overall brain health.
In addition to aerobic activities, residents can consider incorporating strength training exercises into their weekly regimen. Resistance training has been linked to enhanced executive functions, memory, and overall cognitive performance. Joining local fitness classes or utilizing online platforms can help individuals stay motivated and accountable in their pursuit of physical activity. This variety not only keeps routines fresh but also targets different aspects of physical fitness that contribute to cognitive benefits.
Moreover, outdoor activities such as hiking, cycling, or even gardening provide dual benefits by combining physical exertion with the calming effects of nature. Studies suggest that exposure to natural environments enhances mood and reduces stress, further aiding cognitive function. By making outdoor physical activities a priority, individuals can create a more balanced and enriching lifestyle that nourishes both body and mind.
Finally, it is essential to remain consistent and patient. The cognitive benefits of physical activity grow over time, so it's crucial not to get discouraged if results aren't immediately apparent. Keeping track of progress and celebrating small achievements can encourage continued engagement in physical activity. By prioritizing personal health and well-being, individuals can enjoy a sharper mind and a more fulfilling life.
The Importance of Sleep for Mental Clarity

Understanding Sleep Stages and Their Impact on Cognitive Function
Sleep is not a uniform experience; it consists of various stages that play distinct roles in maintaining cognitive function and mental clarity. The two primary categories of sleep, REM (Rapid Eye Movement) and non-REM sleep, both contribute differently to our cognitive abilities. REM sleep is particularly crucial for memory consolidation, problem-solving skills, and emotional regulation. In contrast, non-REM sleep, especially the deep stages, offers restorative benefits to our brains and bodies. A comprehensive understanding of these stages can enhance our sleep quality and overall cognitive performance.
During REM sleep, brain activity mimics that of being awake, which allows us to process emotions, integrate memories, and facilitate learning. Individuals who experience sufficient REM sleep are likely to have better mood stability and more robust decision-making skills. Furthermore, the lack of REM sleep can lead to impaired focus and decreased creativity, impacting personal and professional productivity levels. Relying solely on non-REM sleep without adequate REM phases may not lead to optimal outcomes for mental agility.
In the non-REM stages, particularly during deep sleep, the body enters a restorative state where the brain cleanses itself of toxins and reorganizes information. This process facilitates clearer thinking and enhances overall cognitive capabilities. Skipping or shortening these critical phases could lead to chronic sleep deprivation, which is often associated with long-term cognitive decline and other mental health issues. Therefore, striving for a full cycle of sleep that includes both REM and non-REM stages is essential for sustaining cognitive clarity.
Research indicates that irregular sleep patterns disrupt the delicate balance between REM and non-REM sleep, complicating the restoration and consolidation processes. Consequently, this disruption may lead to cognitive deficits such as memory lapses and slowed problem-solving abilities. It has been shown that those with consistent sleep schedules experience enhanced focus and sharper reasoning skills compared to their more irregular counterparts. Thus, understanding the science behind sleep stages is foundational for enhancing cognitive abilities through improved lifestyle choices.
The Relationship Between Sleep Quality and Mental Health
Sleep quality directly correlates with mental health, influencing everything from mood stability to stress resilience. A lack of quality sleep has been linked to increased anxiety levels and a higher risk of developing mood disorders such as depression. Individuals experiencing chronic sleep deprivation may find themselves trapped in a vicious cycle where poor sleep exacerbates mental health issues, and these issues further complicate sleep quality. Ensuring adequate and restorative sleep is thus paramount for maintaining both mental clarity and emotional well-being.
The connection between sleep and mental health is particularly evident among those who have experienced trauma or chronic stress. Such individuals often struggle with sleep disorders, which, in turn, negatively impact their cognitive functions. Strong evidence suggests that improving sleep hygiene can lead to significant improvements in anxiety and depressive symptoms. Engaging in practices that promote better sleep can serve as a natural and effective method to boost overall mental health.
Moreover, sleep quality can serve as a barometer for cognitive performance. Those who consistently obtain deep and restful sleep demonstrate heightened creative thinking and problem-solving skills. Quality sleep fosters an environment where the brain can effectively manage emotions, thus facilitating more resilient mental states. Understanding this relationship encourages individuals to prioritize sleep as a vital component of a healthy lifestyle that supports not only cognitive functions but also emotional and mental health.
Lastly, focusing on sleep as a critical lifestyle choice can yield long-term cognitive benefits. It encourages individuals to create routines that foster better sleep habits, such as limiting screen time before bed, managing stress levels, and ensuring a comfortable sleeping environment. These measures can significantly improve both the quality and duration of sleep, yielding benefits that extend well beyond the pillow. As research continues to evolve, prioritizing sleep remains an essential strategy for enhancing mental health and cognitive abilities.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Sleep Hygiene
Improving sleep hygiene is crucial for those looking to enhance their mental clarity. Simple habits can significantly impact sleep quality and, by extension, cognitive performance. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, such as reading or meditative practices, can signal to the body that it is time to wind down. Additionally, limiting caffeine intake, particularly in the afternoon and evening, can improve the ability to fall and stay asleep, contributing to a more restful night.
The sleeping environment also plays a significant role in sleep quality. A dark, quiet, and cool room can facilitate better sleep, while excessive noise and light can disrupt the natural sleep cycle. Investing in quality bedding and blackout curtains can prove beneficial for fostering a calming sleep environment. Another important aspect is keeping electronic devices out of the bedroom to minimize distractions and blue light exposure, which can hinder the body's natural circadian rhythms.
Active lifestyle choices also contribute to enhanced sleep hygiene. Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality and duration, leading to better cognitive performance during waking hours. However, it is crucial to time exercise properly; engaging in vigorous workouts too close to bedtime might have the opposite effect, making it harder to relax. Establishing a balanced routine that incorporates regular exercise while still allowing for sufficient wind-down time can enhance both sleep and cognitive clarity.
Mindfulness and stress-reduction techniques are also valuable for improving sleep hygiene. Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can manage anxiety levels, making it easier to sleep peacefully. Learning how to calm the mind before bedtime fosters a state conducive to slipping into restorative sleep. Individuals who incorporate these techniques into their nightly routines often report improvements in their mental clarity and stress management.
The Long-term Benefits of Prioritizing Sleep for Cognitive Health
Prioritizing sleep has profound long-term benefits for cognitive health. Research indicates that consistent, quality sleep enhances memory retention and supports learning. As our brains continue to process information and form new connections during sleep, individuals who routinely allocate time for rest may find themselves more adept at acquiring and utilizing new skills and knowledge. By investing in restorative sleep, one can create a solid foundation for a brighter intellectual future.
Moreover, sleep is integral in warding off age-related cognitive decline. Numerous studies have found a link between inadequate sleep and conditions like dementia and Alzheimer's disease. When we prioritize sleep, we not only optimize our daily cognitive functions but also take proactive steps to safeguard our mental faculties over time. Maintaining healthy sleep patterns can lead to a significant reduction in cognitive decline risk, ensuring sustained intellectual capabilities throughout life.
Engaging in proper sleep hygiene and prioritizing quality rest can enhance mood and emotional resilience. A well-timed sleep schedule promotes emotional processing and stabilizes mood swings. For instance, individuals who uphold healthy sleep habits often report feeling more positive and energized, impacting their daily interactions and overall quality of life. Mental clarity gained from ample sleep allows people to navigate daily challenges with a composed mindset, underscoring the intricate connection between sleep and emotional health.
Ultimately, by making sleep a priority, individuals support not just their cognitive abilities but also their overall health and well-being. Long-term investments in sleep can enhance productivity, creativity, and decision-making skills. As we cultivate a lifestyle that reveres adequate rest, we pave the way for a mentally healthy and productive life.
Mental Stimulation: Keeping the Brain Active

Understanding Mental Stimulation
Mental stimulation refers to activities that engage the brain, challenging it to think and solve problems. This engagement can take many forms, such as puzzles, reading, or learning new skills. Research indicates that regular mental stimulation can contribute to improved cognitive health, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline as we age. By continually pushing the boundaries of our cognitive abilities, we can maintain a sharper mind and enhanced problem-solving skills.
The benefits of mental stimulation extend beyond just cognitive performance. Engaging the brain has also been linked to emotional well-being and reduces the likelihood of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. Therefore, incorporating a variety of mental challenges into our daily routines is essential for holistic brain health.
Impact of Age on Cognitive Abilities
Aging can influence cognitive abilities, making mental stimulation increasingly important for older adults. As neurons age, they may become less efficient, and connections between them can weaken, leading to slower processing speeds. Incorporating challenges that stimulate the mind, such as learning a new language or participating in memory games, helps maintain those connections. This can lead to a significant difference in cognitive resilience.
It is crucial to understand that while some decline is normal with age, actively engaging in mentally stimulating activities can help counteract this decline. Various studies have shown that older adults who participate in stimulating activities demonstrate lower levels of cognitive decline compared to those who do not, emphasizing the importance of lifelong learning and mental engagement.
Types of Mental Stimulation Activities
Mental stimulation can come in many forms, ranging from playful activities to more serious educational pursuits. Activities such as crossword puzzles, Sudoku, and various brain training apps are enjoyable ways to keep the mind sharp. These engaging puzzles often provide immediate feedback, motivating individuals to keep pushing their cognitive limits. Moreover, they can seamlessly fit into daily routines, making them accessible for everyone.
On the more academic side, attending workshops, enrolling in classes, or participating in book clubs provides structured opportunities for mental engagement. Reading diverse genres stimulates the brain by exposing it to new ideas and perspectives. These activities not only enhance cognitive function but also promote social interaction, which is another critical aspect of mental health.
The Role of Technology in Mental Stimulation
Advancements in technology have transformed how we engage our brains. The digital age offers countless resources for cognitive health improvement, ranging from mobile apps designed for brain training to online courses that allow for self-paced learning. These tools have made it more convenient for individuals to include mental stimulation in their daily lives.
However, with these advancements come potential drawbacks, such as screen fatigue and the risk of over-reliance on technology. It is important to balance screen time with other forms of mental challenge. Engaging in offline activities like reading physical books or playing board games can provide valuable mental stimulation and reduce the negative impacts of prolonged screen exposure.
Creating a Lifestyle that Emphasizes Mental Stimulation
To enhance cognitive abilities, one must develop a holistic lifestyle that prioritizes mental stimulation. Establishing a daily routine that includes dedicated time for activities that engage the brain can yield significant benefits over time. Including diverse types of mental challenges ensures that different cognitive functions are exercised. Routine and novelty together provide an optimal environment for maintaining brain health.
Moreover, incorporating physical exercise and social interaction into daily life complements the brain's need for stimulation. Regular physical activity has been shown to enhance brain health by improving blood flow and encouraging the growth of new neurons. Pairing mental and physical activities creates a well-rounded approach for cognitive resilience, reinforcing the mind-body connection crucial for overall well-being.