Why Sufficient Sleep is Essential for Brain Function, Emotional Well being, and Immune System Strength
Mar 01, 2025 / zsfcdn103/
The Impact of Sleep on Cognitive Function
Understanding Sleep Stages and Their Role
Sleep is composed of different stages, primarily divided into REM (Rapid Eye Movement) and non-REM sleep. Each stage plays a crucial role in how our brain functions. During non-REM sleep, particularly stages 3 and 4, the body undergoes restorative processes that are vital for cognitive performance. In contrast, REM sleep is essential for memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and creativity. Understanding these stages helps highlight why adequate sleep is indispensable for optimal brain operation.
The sleep cycle lasts approximately 90 minutes, cycling through these stages multiple times each night. A healthy adult typically experiences four to six cycles of sleep per night. Disruption in these cycles adversely affects cerebral functions, such as attention, problem-solving skills, and decision-making. Thus, a consistent sleep routine that allows for complete cycles is critical for maintaining cognitive sharpness and strong mental acuity.
It’s important to recognize that sleep quality can be just as significant as quantity. Factors such as sleep disorders, environmental disturbances, or irregular sleeping patterns can lead to fragmented sleep. Such fragmentation inhibits the brain's ability to progress through necessary sleep stages, leading to poorer cognitive outcomes. Therefore, understanding sleep stages can inform better practices for enhancing cognitive function through improved sleep hygiene.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Performance
Sleep deprivation has been shown to significantly impair various cognitive functions, including attention span, task performance, and decision-making. When individuals do not get sufficient rest, they may experience lapses in focus and an inability to process information effectively. Research consistently shows that even small reductions in sleep can lead to marked declines in cognitive abilities, rivalling the effects of intoxication.
Moreover, chronic sleep deprivation can result in long-term cognitive deficits. Studies reveal that those who suffer from sleep issues over extended periods display weakened neural connections, particularly in regions of the brain responsible for memory and executive functions. This decline can impact everyday tasks and responsibilities, making it increasingly challenging to function both at work and in personal life.
Interestingly, the effects of sleep deprivation are not uniform across all individuals. Factors such as age, baseline cognitive function, and overall health play a role in how severely one may experience cognitive impairments due to lack of sleep. However, the overarching consensus remains: prioritizing adequate sleep is fundamental for maintaining high cognitive performance across different populations and age groups.
The Connection Between Sleep and Emotional Well-being
Adequate sleep is intrinsically linked to emotional stability and overall mental health. During sleep, especially during REM stages, the brain processes emotional experiences, helping to mitigate stress and anxiety. Insufficient sleep disrupts this process, leading to emotional dysregulation, increased irritability, and a higher likelihood of developing mood disorders such as depression or anxiety.
Notably, individuals who regularly sleep poorly are significantly more likely to exhibit symptoms of emotional distress. This can lead to a vicious cycle where poor emotional health further disrupts sleep, compounding the issues. Prioritizing sleep can thus serve as a protective factor for emotional resilience, enabling individuals to manage stress more effectively.
Furthermore, sleep influences interpersonal relationships and social interactions. When well-rested, individuals tend to exhibit improved empathy, awareness, and communication skills. Conversely, lack of sleep can lead to misunderstandings and conflict in relationships, which may exacerbate feelings of isolation or loneliness. Understanding the emotional benefits of sound sleep encourages individuals to adopt healthier sleep habits, enhancing both individual well-being and social dynamics.
Sleep's Role in Immune Function and Overall Health
Research indicates a profound relationship between sleep quality and immune system strength. During sleep, the body produces cytokines, proteins that play a vital role in the immune response. Insufficient sleep can hinder the production of these crucial proteins, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. This illustrates the necessity of adequate sleep for maintaining overall health and combating disease effectively.
Additionally, sleep deprivation has been directly linked to increased inflammation in the body, which can lead to numerous health problems, including cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. By fostering a healthy sleep routine, individuals enhance their immune defense mechanisms, leading to improved overall physical health and greater resistance against chronic ailments.
The synergistic relationship between sleep and health underscores the holistic nature of well-being. Individuals prioritizing their sleep not only boost their cognitive and emotional health but also fortify their physical well-being. Investing in good sleep habits serves as an essential pillar in a comprehensive approach to health maintenance, emphasizing the integral role that sleep plays in our lives.
Practical Tips for Improving Sleep Quality
For those looking to enhance their sleep quality, several strategies can be effectively employed. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule is one of the most straightforward and effective methods. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate the body's internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up refreshed. Consistency plays a critical role in ensuring that the brain receives the restorative sleep it requires for optimal functioning.
Creating a conducive sleeping environment is also crucial. Dimming lights, reducing noise, and ensuring a comfortable temperature can vastly improve sleep quality. Investing in supportive mattresses and comfortable bedding can further enhance the sleeping experience, allowing individuals to enjoy uninterrupted restful nights.
Finally, cultivating bedtime rituals can signal the brain that it’s time to wind down—this can include reading, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Minimizing exposure to electronic devices before bed is also essential, as the blue light emitted by screens can interfere with melatonin production, thus complicating the process of falling asleep. These holistic practices empower individuals to reclaim the quality sleep essential for mental, emotional, and physical well-being.
Sleep's Role in Mood Regulation
Understanding the Connection Between Sleep and Emotional Health
The relationship between sleep and emotional health is intricate and deeply rooted in our biological makeup. Research consistently shows that inadequate sleep can lead to heightened levels of stress and anxiety, making it challenging to manage negative emotions. When we are sleep-deprived, our brains are unable to process experiences effectively, leading to emotional dysregulation.
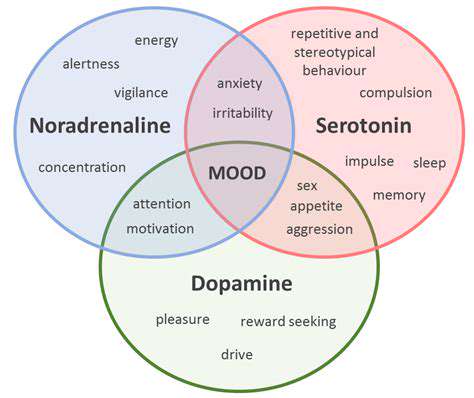
Furthermore, the impact of sleep on mood can also be attributed to its influence on neurotransmitters that regulate emotions. Neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine are crucial for maintaining emotional balance. When sleep is disrupted, the production of these critical chemicals can be impaired, contributing to mood disorders such as depression.
Finally, understanding this connection underscores the importance of maintaining healthy sleep patterns. Individuals seeking to improve their mental health and emotional stability must prioritize sleep as a key component of their overall wellness strategy. Creating a conducive sleep environment and establishing a regular sleep schedule can significantly enhance mood regulation.
Strategies to Enhance Sleep Quality for Better Mood Regulation
Improving sleep quality is essential for mood regulation, and there are several strategies that individuals can utilize to achieve this goal. One effective method is to establish a calming pre-sleep routine, which signals the body that it is time to wind down. Activities such as reading, meditating, or taking a warm bath can promote relaxation and make it easier to fall asleep.
Another important aspect to consider is the sleep environment. Creating a dark, quiet, and cool sleeping space can significantly enhance sleep quality, leading to restful nights. Incorporating blackout curtains, white noise machines, or air purifiers can transform an ordinary bedroom into a sleep sanctuary.
Finally, being mindful of lifestyle choices that contribute to sleep quality is crucial. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and reducing screen time before bed can all positively affect how well you sleep. Emphasizing these strategies can improve sleep quality, which subsequently supports better emotional health and resilience.
The Connection Between Sleep and Immune Health
The Role of Sleep in Immune Response
Sleep is a critical component of the immune system's ability to function efficiently and effectively. During sleep, the body undergoes a series of restorative processes that help in the production and release of proteins known as cytokines. These cytokines are crucial for the immune response, as they facilitate communication between immune cells and enhance the body's ability to fight off infections and inflammation. Lack of sleep can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to an increased risk of illness.
Moreover, inadequate sleep can result in a decline in the production of antibodies and immune cells, which play vital roles in defending the body against pathogens. This decline makes individuals more susceptible to viruses and bacteria, underscoring the importance of obtaining sufficient rest to maintain a robust immune system. The regular release of growth hormones during sleep also contributes to recovery, providing the necessary resources for immune cells to thrive.
Research has shown that people who consistently sleep less than six hours a night are more likely to catch a cold when exposed to the virus, highlighting the direct connection between sleep duration and immune resilience. By prioritizing sleep, individuals can bolster their immune responses, enabling them to combat infections more effectively and reduce the frequency of illnesses.
In conclusion, sleep plays a formidable role in the immune system by enhancing the body's ability to respond to infections and recover from illnesses. A consistent sleep schedule not only supports individual health but also promotes overall wellness by allowing the immune system to function optimally. To improve immune health, individuals should focus on establishing healthy sleep habits, ensuring they allocate enough time for restful sleep.
How Sleep Quality Affects Immune Function
The quality of sleep is just as crucial as the quantity when it comes to maintaining a healthy immune system. Restorative sleep cycles contribute to the body's ability to recover and rejuvenate. During deep sleep phases, the body experiences reduced cortisol levels, minimizing stress that can otherwise weaken immune responses. Disruptions to these sleep cycles, such as insomnia or frequent awakenings, can impair immune functionality.
Adequate REM sleep is essential for cognitive processes and emotional regulation, which can indirectly influence immune health. Disruptions in sleep quality can lead to heightened stress levels, which in turn can trigger an inflammatory response within the body. This chronic inflammation can weaken immune functions over time, making it crucial for individuals to focus not just on how long they sleep, but on how well they achieve deeper and uninterrupted sleep cycles.
Additionally, factors such as sleep environment, nutritional habits, and daily routines can have significant impacts on sleep quality. For example, reducing blue light exposure from digital devices before bedtime can significantly improve both the onset of sleep and the quality thereof. Creating a serene sleep environment free from noise and distractions can facilitate deeper sleep and promote better overall health.
Ultimately, the correlation between sleep quality and immune function cannot be overstated. Individuals should actively seek to enhance their sleep hygiene, fostering an environment and lifestyle conducive to high-quality sleep. By prioritizing both the duration and quality of sleep, individuals can significantly strengthen their immune health and improve their resilience against illness.