The Challenge of Relaxation: How Physiological Responses Impact Sleep Quality
Nov 14, 2024 / zsfcdn103/
Introduction to Physiological Responses and Sleep
Understanding the Connection Between Stress and Sleep
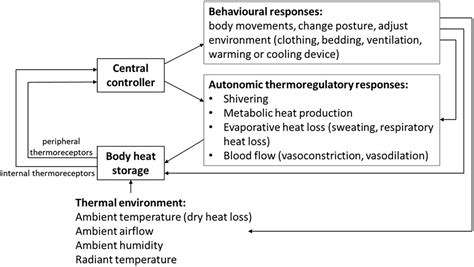
Stress is a common experience in our daily lives, and it has a profound effect on our physiological responses. When we encounter stress, our body undergoes a series of changes known as the stress response. This response is designed to help us deal with threats, but it can also cause long-term issues when stress becomes chronic. Research indicates that chronic stress can lead to difficulties falling asleep and staying asleep. Understanding how stress impacts sleep is the first step towards improving sleep quality.
One of the primary physiological responses to stress is the release of cortisol, a hormone that can disrupt our natural sleep cycle. High levels of cortisol during the night can make it difficult to reach the deeper stages of sleep, which are essential for restorative rest. This disruption can lead to a cycle of sleep deprivation that exacerbates stress levels. Gaining insight into this cycle can be vital for those struggling with sleep disorders.
In addition to cortisol, stress can also cause the body to produce adrenaline, which prepares us for 'fight or flight' responses. This heightened state can make it nearly impossible to relax and wind down at night. Effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, can be beneficial in breaking this cycle. Establishing a consistent relaxation routine before bed can aid in lowering both cortisol and adrenaline levels.
Moreover, stress-related physiological responses may also trigger behavioral changes that impact sleep. When people are stressed, they might resort to caffeine or alcohol consumption as coping mechanisms, which can further disrupt sleep patterns. Thus, addressing both physiological and behavioral factors is essential in a comprehensive approach to improving sleep quality.
In summary, the intricate connection between stress and sleep reveals that managing stress is crucial for achieving better sleep quality. Implementing healthy stress management practices can result in significant improvements in sleep health. Understanding this relationship empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward better sleep hygiene.
Physiological Factors Affecting Sleep Architecture
Sleep architecture refers to the structure and pattern of sleep cycles throughout the night, which consists of different stages, including REM and non-REM sleep. These stages play a vital role in physical recovery and mental restoration. Disruptions to this architecture can lead to a fragmented sleep experience. Various physiological factors can significantly affect the quality of sleep architecture.
Temperature regulation is one such physiological factor that can influence sleep. Our bodies naturally cool down to signal that it's time for sleep, and disruptions in this process can lead to wakefulness. Maintaining a comfortable sleeping environment can enhance the body's ability to regulate temperature, facilitating better sleep. Small adjustments like using breathable bedding or controlling room temperature can create ideal sleeping conditions.
Circadian rhythms, or our internal biological clock, also play a crucial role in sleep architecture. These rhythms are influenced by external cues like light and darkness and can be disrupted by irregular sleep patterns. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule helps to reinforce these rhythms, thus promoting more robust and uninterrupted sleep cycles.
In addition, medical conditions such as sleep apnea can adversely affect sleep architecture by causing interruptions in breathing during sleep. This can lead to frequent awakenings and an inability to reach restorative sleep stages. Addressing underlying health issues is essential for ensuring healthy sleep architecture. Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals can help manage these conditions effectively.
Ultimately, understanding the physiological factors that influence sleep architecture can empower individuals to implement changes that enhance their sleep quality. Recognizing the importance of creating a conducive sleeping environment, managing circadian rhythms, and addressing medical issues can lead to a more restorative sleep experience.
Impact of Food and Nutrition on Sleep Quality
The relationship between diet and sleep quality is an area of growing interest among researchers and health professionals. Certain foods can positively or negatively influence sleep patterns, impacting overall sleep quality. For instance, high caffeine intake is known to interfere with the ability to fall asleep, emphasizing the need for mindful consumption, especially in the hours before bedtime.
On the other hand, foods that are rich in tryptophan, such as turkey and nuts, can aid in the production of serotonin and melatonin, hormones that regulate sleep. Incorporating such foods into your diet may support better sleep. Additionally, a balanced diet that includes vitamins and minerals can contribute to overall health and well-being, indirectly benefitting sleep quality. Hydration also plays a crucial role; however, excessive fluid intake close to bedtime can lead to nighttime awakenings.
Moreover, the timing of meals can impact sleep. Eating large meals late at night can cause discomfort and indigestion, leading to poor sleep quality. It is generally advised to aim for lighter meals closer to bedtime to minimize discomfort and ensure a more restful night. Establishing a routine around meal times can help signal to the body that it’s preparing for sleep.
Alcohol consumption presents another dual-edged factor influencing sleep quality. While it might help individuals fall asleep faster, it often disrupts later stages of sleep, leading to less restorative rest. Being mindful of alcohol consumption and recognizing its impact on sleep can help individuals make more informed choices regarding their evening routines.
In conclusion, the interplay between food, nutrition, and sleep quality is complex. Recognizing how dietary choices affect sleep patterns may encourage individuals to adopt healthier eating habits that promote better sleep. Adjusting caffeine intake, meal timing, and food choices can lead to significant improvements in sleep quality.
The Role of Exercise in Enhancing Sleep Quality
Regular physical activity has been shown to have numerous benefits for overall health, including improved sleep quality. Exercise helps to reduce stress and anxiety, which are common barriers to restful sleep. Research indicates that individuals who engage in regular physical activity tend to fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper sleep compared to those who are sedentary. Thus, the role of exercise in enhancing sleep cannot be understated.
The timing of exercise is also crucial for its impact on sleep. While some individuals may find that exercising too close to bedtime makes it harder to wind down, others may experience a boost in sleep quality regardless of timing. Generally, moderate exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling performed during the day can lead to better sleep outcomes. Establishing a consistent exercise routine can help regulate sleep patterns and improve overall health.
Additionally, exercise can enhance the body’s natural circadian rhythms, helping to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Being active during daylight hours exposes the body to natural light, which plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy circadian rhythms. This natural exposure can promote better sleep at night, making a strong case for incorporating outdoor activities into one's routine.
Furthermore, specific types of exercise can be particularly effective in promoting relaxation and preparing the body for sleep. Gentle activities like yoga and stretching can help to ease tension in the body and mind, promoting a state of relaxation that is conducive to sleep. Incorporating these mindful movements into your evening routine may significantly enhance sleep quality.
In summary, exercise plays a vital role in promoting better sleep quality through various mechanisms. Regular physical activity, combined with mindful movement practices, creates an environment that is conducive to relaxation and restorative sleep. Making exercise a priority can lead to lasting improvements in sleep hygiene.
Creating the Ideal Sleep Environment
The environment in which we sleep can have a profound impact on sleep quality. Factors such as light, noise, temperature, and comfort should be considered when creating a sleep-friendly environment. Optimizing the sleep environment can significantly enhance the ability to fall asleep and remain asleep throughout the night.
Light exposure plays a pivotal role in regulating our sleep-wake cycles. It is essential to create a dark sleeping environment, as exposure to light can signal the brain that it's time to be awake. Investing in blackout curtains or using eye masks can help to eliminate light interference, promoting a more restful night’s sleep.
Noise is another factor that can disrupt sleep. Many individuals may benefit from white noise machines or earplugs to cancel out disruptive sounds. Creating a quieter environment can significantly reduce the likelihood of nighttime awakenings and enhance overall sleep quality. Being mindful of external noise sources is important for creating an optimal sleep environment.
Temperature regulation is also critical for sleep comfort. Most individuals sleep best in cooler rooms, so it’s advisable to keep the bedroom temperature between 60-67 degrees Fahrenheit. Consideration of bedding materials and sleepwear can also impact temperature regulation, leading to a more comfortable night’s rest.
Finally, comfort plays a crucial role in creating a conducive sleep environment. Investing in a comfortable mattress and supportive pillows can greatly affect sleep quality. Tailoring your sleep setup to meet personal preferences can facilitate deeper sleep and a more refreshing rest. In conclusion, creating the ideal sleep environment is key to improving sleep quality and overall well-being.
The Body's Stress Response
The Mechanisms of Stress Response
When faced with a stressor, the body initiates a series of physiological changes known as the stress response. This includes the release of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which prepare the body to react quickly to threats. These hormones increase heart rate, elevate blood pressure, and boost energy supplies, creating a state of heightened alertness.
While this response is crucial for survival, it can become problematic when activated chronically due to ongoing stressors like work pressure or personal issues. Prolonged exposure to high levels of stress hormones can lead to various health issues, including anxiety and sleep disturbances.
The nervous system plays a significant role in this process, with the sympathetic nervous system being activated during stress. This activation can inhibit the body's ability to relax, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep during the night.
Additionally, the body’s stress response can cause muscle tension and discomfort, which further complicates efforts to rest and recover. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for developing strategies to mitigate their effects.
Ultimately, learning to regulate the stress response through various techniques can improve not only emotional well-being but also physical health and sleep quality.
Impact of Stress on Sleep Quality
The interrelationship between stress and sleep is well-documented, with rising stress levels often correlating with declining quality of sleep. Chronic stress can lead to insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking too early.
During stressful periods, individuals may find themselves preoccupied with worries or racing thoughts as they attempt to wind down for the night. This mental agitation makes it incredibly challenging to achieve the calm needed for restful sleep.
Moreover, elevated cortisol levels can disrupt the body's natural circadian rhythm, further complicating sleep patterns. It signals to the body that it’s time to remain alert rather than relax.
Sleep architecture can also be affected, with people experiencing reduced time in restorative sleep stages, such as deep sleep and REM sleep. This can lead to fatigue, mood disturbances, and decreased cognitive performance during the day.
Recognizing the specific ways that stress deteriorates sleep quality is essential to identify effective interventions aimed at promoting better sleep health.
Coping Strategies for Stress Management
Effectively managing stress is vital for improving sleep quality and overall health. One widely recommended approach is practicing mindfulness and meditation, which can reduce stress levels and promote relaxation.
Engaging in regular physical activity is another effective strategy, as exercise helps to regulate hormones, reduce tension, and improve overall well-being. Even moderate exercise, such as walking or yoga, can yield significant benefits for stress management.
Establishing a consistent sleep routine can also enhance relaxation. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps to reinforce the body's internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep when the time comes.
Additionally, deep breathing techniques can be beneficial. Practicing deep, concentrated breaths signals the body to slow down and calms the nervous system, preparing it for sleep.
Lastly, seeking social support by talking to friends, family, or professionals about stressors can provide relief and new perspectives on managing challenges.
The Role of Environment in Sleep Quality
Creating a relaxing sleep environment can significantly impact one’s ability to unwind and drift off to sleep. Dim lighting, a comfortable mattress, and a quiet atmosphere can help signal to the body that it’s time for rest.
Temperature control is also crucial; a cool room is generally recommended as it can encourage better sleep. Overheating can lead to restlessness, disrupting sleep cycles.
Incorporating calming scents, such as lavender or chamomile, through essential oils or candles can promote relaxation and signal to the brain that it’s time to calm down.
Eliminating distractions like screens and noise contributes to an optimal sleep environment as they can interfere with the natural production of sleep hormones.
By enhancing the sleep environment, individuals can create a sanctuary for rest, leading to improved sleep quality and better response to stressors.
Long-term Effects of Poor Sleep on Health
Chronic poor sleep quality can lead to a myriad of long-term health consequences. It is associated with an increased risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease, obesity, and diabetes.
Moreover, inadequate sleep has been linked to mental health issues, particularly anxiety and depression. The cycle of stress and sleep deprivation can exacerbate these conditions, creating a challenging feedback loop.
Cognitive performance can also decline with prolonged poor sleep, resulting in memory issues, difficulty concentrating, and decreased problem-solving abilities. This impacts job performance and daily activities, leading to further stress.
Furthermore, lack of restorative sleep can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illness and slowing recovery from existing conditions.
Addressing sleep quality and its association with stress is crucial not only for immediate well-being but also for fostering long-term health resilience.
The Impact of Anxiety on Sleep
The Connection Between Anxiety and Sleep Quality
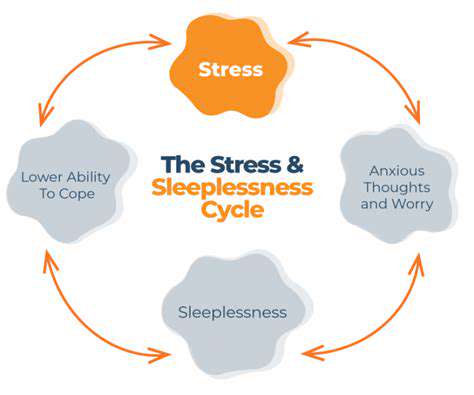
Anxiety is a widespread issue that can significantly affect sleep patterns. It triggers a range of physiological responses, including increased heart rate and heightened alertness, making it challenging to relax. When an individual is anxious, their body remains in a state of heightened arousal, which can lead to insomnia or restless sleep. The constant worry exacerbates sleep disturbances, creating a vicious cycle. As a result, those affected often find it hard to unwind at bedtime, leading to poor sleep quality.
Studies have shown that individuals with anxiety disorders frequently experience sleep disturbances. These disturbances can manifest as difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings, and early morning awakenings. The brain remains active during the night, replaying anxious thoughts, which interferes with deep sleep stages. Over time, consistent lack of sleep can worsens anxiety, leading to a lack of concentration, increased irritability, and overall poor mental health.
It’s essential to understand the interplay between anxiety and sleep quality to address this challenge effectively. Techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy specifically aimed at insomnia can help alleviate sleep issues. By managing anxious thoughts, patients can improve their sleep patterns substantially. Additionally, mindfulness practices have been shown to reduce anxiety levels, promoting a more restful night.
Approaching sleep with relaxation techniques can be beneficial. Things like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can lower heart rate and calm the mind. Implementing these strategies consistently can dramatically improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety levels over time. It’s not just about the hours spent sleeping but the quality of that sleep and its restorative effects on the body and mind.
Physiological Responses to Stress and Their Effects on Sleep
A study showed that chronic stress can lead to changes in sleep patterns, such as reduced rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep is crucial for emotional regulation and memory consolidation; thus, its deprivation can affect overall well-being. Those who experience high levels of stress often report feeling unrefreshed upon waking, further exacerbating feelings of anxiety and fatigue.
Additionally, physiological responses can lead to physical symptoms that hinder sleep. Muscle tension and discomfort can arise from stress, resulting in difficulty in finding a comfortable sleep position. This discomfort can make it challenging to fall asleep or stay asleep, creating a negative feedback loop that can diminish sleep quality.
Addressing physiological responses to stress is crucial for improving sleep quality. Incorporating practices like yoga, stretching, or gentle physical activity into daily routines can help release tension. Such interventions not only promote relaxation but also encourage better sleep habits, contributing to overall health and well-being. A multifaceted approach is often necessary to break the cycle of stress and enhance sleep quality.
The Role of Sleep Hygiene in Managing Anxiety
Sleep hygiene refers to a set of practices designed to promote consistent, uninterrupted sleep. Good sleep hygiene can be instrumental in managing anxiety and improving overall sleep quality. By creating a conducive sleep environment, individuals can help regulate their sleep patterns effectively. This includes maintaining a quiet, dark, and cool bedroom to help signal to the body that it's time to sleep.
Establishing a regular sleep schedule is another key aspect of good sleep hygiene. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps to regulate the body's internal clock. This consistency aids in easing anxiety by providing structure and predictability, which can be comforting. Most importantly, limiting the use of screens before bedtime can reduce the exposure to blue light, which is known to interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone essential for sleep.
In addition to creating a calming environment, the activities leading up to bedtime can influence sleep quality. Engaging in relaxing activities, such as reading or taking a warm bath, can help to signal the body that it's time to wind down. Avoiding stimulating activities such as intense exercise or consuming caffeine in the hours before bed can help facilitate a smoother transition to sleep. Paying attention to these factors can drastically improve both sleep quality and reduce anxiety levels.
It's also beneficial to develop a bedtime routine that encourages relaxation. This can include practices like journaling to get anxious thoughts out of one’s mind before sleep. Establishing rituals such as gentle stretching or listening to soothing music can create a calming atmosphere that promotes restful sleep. Making sleep hygiene a priority can contribute significantly to managing anxiety and enhancing overall sleep quality.
Biological Mechanisms Linking Sleep and Anxiety
The biological mechanisms that link sleep and anxiety are complex and multifaceted. Sleep deprivation can lead to dysregulation in neurotransmitter systems that play a role in mood regulation. When these systems are affected, it can heighten feelings of anxiety, leading to a detrimental cycle impacting overall mental health. Specifically, reduced levels of serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) – neurotransmitters that promote calmness and relaxation – can worsen anxiety symptoms.
Furthermore, disrupted sleep can alter the brain's structure and function over time, impacting areas responsible for emotional regulation, including the amygdala. The amygdala is hyperactive in those who experience anxiety, which can result in exaggerated responses to stressors. This neurobiological perspective underscores the importance of prioritizing good sleep in the overall treatment of anxiety disorders.
Chronic anxiety can lead to sleep disorders, which further distorts sleep architecture, impacting critical sleep stages like deep sleep and REM sleep. Consequently, this disruption can impair cognitive functions such as memory and decision-making, making it even harder to manage anxiety during waking hours. Addressing both anxiety and sleep simultaneously is necessary for effective treatment. Behavioral interventions can target both aspects to create a more holistic approach.
In conclusion, understanding the biological interplay between sleep and anxiety is essential for identifying effective management strategies. Improving sleep may help to stabilize mood and reduce anxiety levels, while managing anxiety can lead to better sleep outcomes. This reciprocal relationship highlights the need for integrated approaches that address both symptoms.
Effective Strategies for Enhancing Sleep Quality in Anxious Individuals
Enhancing sleep quality in individuals with anxiety requires a tailored approach that acknowledges personal triggers and stressors. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective, focusing on changing negative thought patterns associated with anxiety and sleep. Cognitive restructuring combats irrational fears and negative beliefs about sleep, paving the way for improved sleep quality. Over time, this technique can lead to a reduced experience of anxiety during nighttime hours.
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques play a crucial role in lowering anxiety and improving sleep. Practices such as guided imagery, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation help individuals calm racing thoughts and bring their attention back to the present moment. Implementing these strategies regularly, especially before bedtime, can enhance the ability to fall asleep and stay asleep, creating a more restorative sleep experience.
Additionally, establishing a supportive social environment can be beneficial. Close connections with friends and family members can provide emotional support to navigate anxiety's challenges. Having people to talk to during anxious moments can alleviate stress and subsequently improve sleep patterns. Community connection is an essential component of building resilience against anxiety.
Lastly, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding alcohol or recreational drug use can create a solid foundation for better sleep. Physical health directly impacts mental health, so the synergy between the two should never be underestimated. By committing to healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can significantly enhance their sleep quality and better manage anxiety.
Techniques to Manage Physiological Responses

Breathing Exercises
Breathing exercises are a fundamental technique to help manage physiological responses that can hinder sleep quality. These exercises can reduce stress and anxiety levels by stimulating the body’s relaxation response. By focusing on deep, slow breaths, individuals can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes a state of calmness.
Incorporating breathing exercises into a nightly routine can be highly effective. For instance, techniques such as the 4-7-8 breathing technique encourage a focus on counting and rhythm, which can distract from racing thoughts. This method not only prepares the body for restful sleep but also helps maintain emotional balance.
Additionally, practicing these methods consistently can lead to long-term improvements in sleep quality. As individuals become more familiar with their breathing patterns, they can use these skills to manage triggers of stress or anxiety more effectively. Overall, proper breathing techniques serve as a powerful tool for enhancing overall well-being.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) is another effective strategy for reducing physiological tension. This technique involves tensing and then relaxing each muscle group in the body, promoting a physical state of tranquility. Practicing PMR encourages awareness of bodily sensations and helps individuals distinguish between tension and relaxation.
During each session, one might start from the toes and gradually move up to the head, focusing on breathing and tension release. By concentrating on the contrast between tensed and relaxed muscles, individuals can significantly decrease their overall stress levels. Regular sessions of PMR can greatly enhance an individual's ability to unwind before bed.
Moreover, PMR can be particularly beneficial for those struggling with insomnia or anxiety-related sleep disturbances. Developing a connection with one's body can help individuals recognize when they are feeling physically tense and consciously release that tension. As a result, PMR can be a key component of a holistic approach to improving sleep quality.
Meditation and Mindfulness Practices
Meditation and mindfulness practices have been shown to improve sleep quality by reducing rumination and promoting relaxation. These methods encourage individuals to become more aware of their thoughts and emotions without judgment, which can alleviate anxiety surrounding sleep. Establishing a meditation routine can cultivate a peaceful mindset conducive to falling asleep more easily.
Simple techniques such as guided imagery or body scan meditations can be incorporated into pre-sleep routines. These practices help to shift focus away from daily stressors and redirect attention toward calming imagery or sensations. Committing to just a few minutes of meditation before bed can significantly enhance the transition from wakefulness to sleep.
Furthermore, mindfulness practices can help individuals develop better sleep hygiene by fostering habits that promote consistent relaxation. Engaging in meditation regularly can lead to long-term enhancements in emotional well-being, which indirectly benefits sleep quality. As practitioners become more familiar with these introspective techniques, they often find it easier to achieve a state of relaxation at bedtime.