美國CPAP使用情況:關鍵見解和統計數據
May 01, 2025 / zsfcdn103/
Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) in the US
Prevalence Statistics
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a prevalent sleep disorder affecting millions of Americans. While precise figures are difficult to pin down due to varying diagnostic criteria and underreporting, estimates suggest that a significant portion of the US adult population experiences some level of OSA. Factors like age, ethnicity, and gender play a crucial role in the prevalence. Further research and more standardized diagnostic protocols are needed to provide more accurate and comprehensive data on the true scope of OSA in the US population. Current data indicates a significant need for increased awareness and improved diagnostic tools to address this public health concern effectively.
Studies consistently highlight a higher prevalence of OSA in specific demographic groups. For example, men tend to be diagnosed with OSA more frequently than women, particularly during middle age. This difference may be attributed to hormonal factors and anatomical variations. Similarly, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as obesity or hypertension, are at a higher risk of developing OSA. Identifying these risk factors and implementing preventative strategies are crucial for minimizing the impact of this sleep disorder.
Impact on Public Health
The prevalence of OSA has significant implications for public health. The chronic sleep deprivation associated with OSA can lead to a range of adverse health consequences, including cardiovascular issues, type 2 diabetes, and increased risk of accidents. Furthermore, the untreated sleep disorder can contribute to decreased productivity and impaired cognitive function. This underscores the importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment options. Public awareness campaigns, improved access to sleep specialists, and the development of more accessible diagnostic tools are all vital steps in mitigating the public health burden of OSA.
Economic costs associated with OSA are substantial. The increased healthcare utilization, lost productivity, and the direct costs of treatment represent a considerable burden on the US healthcare system. Addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach that combines preventative measures, improved diagnostic capabilities, and access to effective treatment options, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, which is a focal point of this article.
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of OSA and the optimal strategies for prevention and management. This will ultimately lead to better outcomes for individuals affected by OSA and reduce the overall strain on the healthcare system.
Addressing the socioeconomic disparities in OSA prevalence is critical. Factors like access to healthcare, socioeconomic status, and cultural beliefs can contribute to disparities in diagnosis and treatment. Developing culturally sensitive interventions and strategies to improve access to care are crucial for reducing health disparities and ensuring equitable care for all.
The growing awareness of the impact of OSA on public health is driving efforts to improve diagnosis and treatment. This includes the development of more accurate screening tools, increased access to sleep specialists, and the promotion of healthier lifestyle choices to reduce the risk of OSA.
CPAP Adherence Rates and Factors Influencing Success
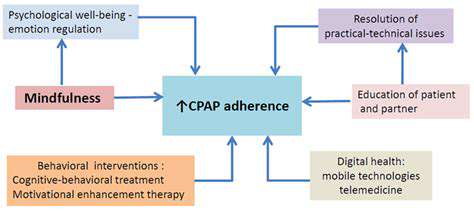
CPAP Adherence and its Importance
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) therapy is a crucial treatment for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a common disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. Effective CPAP therapy significantly improves sleep quality and overall health outcomes for individuals with OSA. However, a significant challenge lies in achieving and maintaining adherence to the prescribed CPAP treatment regimen. High adherence rates are essential for maximizing the therapeutic benefits of CPAP and mitigating the long-term health risks associated with untreated OSA.
Understanding the factors influencing CPAP adherence is critical for developing targeted interventions and support strategies. Poor adherence can lead to a less effective treatment, hindering the positive impact of CPAP on sleep quality and overall health. This, in turn, can result in increased risks of complications related to untreated OSA, such as cardiovascular problems, stroke, and cognitive impairment.
Factors Affecting CPAP Adherence
Several factors contribute to the variability in CPAP adherence rates. These include the complexity and inconvenience of using a CPAP machine, including the need for mask fitting and adjustments, which can sometimes be uncomfortable and lead to skin irritation. The noise level of the CPAP machine can also affect sleep quality and compliance.
Furthermore, the perceived or actual discomfort associated with the therapy, particularly the mask, can discourage continued use. Individuals may also experience difficulty adjusting to the new sleep environment, the need for consistent use, and the perceived effort required to maintain adherence to the therapy. These factors can significantly influence a person's willingness and ability to consistently use the CPAP machine.
The Role of Patient Education and Support
Effective patient education plays a vital role in improving CPAP adherence. Comprehensive information about the benefits of CPAP therapy, the importance of consistent use, and potential side effects can empower individuals to actively participate in their treatment. This includes providing clear instructions on how to operate the CPAP machine, maintain the mask, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Well-structured support groups and counseling can also be very helpful. These can provide a platform for individuals to share experiences, ask questions, and receive encouragement from others facing similar challenges. Support groups can provide valuable insights and strategies for overcoming obstacles and maintaining motivation.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Technological advancements have significantly impacted CPAP therapy, leading to more user-friendly and comfortable devices. The development of quieter CPAP machines, more comfortable masks, and features like automatic pressure adjustments can improve patient tolerance and adherence. This includes advancements in mask designs and materials to reduce pressure points and improve comfort.
Continuous monitoring and feedback systems have further enhanced CPAP therapy by allowing clinicians to assess adherence patterns and provide tailored support. These tools can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the therapy and identify potential barriers to compliance. Furthermore, remote monitoring systems allow for ongoing communication between the patient and healthcare provider, promoting better adherence and outcomes.
Impact of CPAP Adherence on Long-Term Outcomes
High CPAP adherence rates are directly linked to better long-term health outcomes for individuals with OSA. Studies have demonstrated that consistent use of CPAP can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications, improve cognitive function, and enhance overall well-being. It is essential to understand the positive impact of CPAP adherence on sleep quality, daytime alertness, and overall health.
Maintaining consistent adherence to CPAP therapy is crucial for preventing or mitigating the potential long-term health risks associated with untreated OSA. These benefits translate into a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cognitive impairment, highlighting the importance of support and strategies to improve adherence.
Future Trends and Research in CPAP Utilization

Advancements in CPAP Mask Technology
Innovations in CPAP mask design are focusing on enhanced patient comfort and adherence. This includes the development of more lightweight materials and improved seal mechanisms to minimize pressure points and discomfort during sleep. Furthermore, there's a growing trend toward customizable masks, allowing patients to tailor the fit to their unique facial features for optimal therapy efficacy and reduced pressure on sensitive areas.
Researchers are also exploring new mask materials with enhanced breathability and hypoallergenic properties, addressing potential skin irritation issues and improving overall patient experience. This focus on comfort and personalization is crucial in encouraging long-term CPAP adherence.
Personalized CPAP Therapy
The future of CPAP therapy is increasingly personalized. This involves tailoring CPAP settings to individual patient needs, rather than using generic settings. Advanced diagnostic tools and algorithms are being developed to analyze sleep data more precisely, allowing for dynamic adjustments in pressure and other parameters throughout the night. This leads to more effective treatment and better sleep quality.
This personalized approach goes beyond simply adjusting pressure settings. It also incorporates factors like patient lifestyle and comorbidities, further optimizing therapy to address individual needs and potential complications.
Integration of CPAP with Wearable Technology
Integrating CPAP devices with wearable technology is another promising area of research. These devices can track sleep patterns and CPAP usage in real-time, providing valuable data to both patients and healthcare providers. This real-time data analysis allows for more precise monitoring of therapy effectiveness and the identification of potential issues early on.
Wearable technology can also alert patients to issues like leaks or mask adjustments, allowing for prompt intervention and potentially improving treatment outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being employed to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of CPAP therapy. AI algorithms can analyze sleep data, identify patterns, and predict optimal CPAP settings in real-time, leading to more personalized and precise treatment. This approach is expected to improve treatment outcomes and patient adherence.
Furthermore, AI can also be used to identify potential complications or adverse reactions to CPAP therapy, allowing for proactive interventions and improved patient safety.
Remote Patient Monitoring and Telemedicine
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) and telemedicine are playing an increasingly important role in CPAP management. These technologies allow for continuous monitoring of patients' CPAP usage and sleep data from a distance, reducing the need for frequent clinic visits. This approach can also improve patient access to care, particularly in underserved communities.
Telemedicine enables remote consultations with healthcare providers, allowing for prompt adjustments to CPAP settings and addressing any concerns or issues that may arise. This remote interaction also fosters better patient engagement and improves adherence to treatment plans. This is a significant step toward improving the overall CPAP experience.
Research on Long-Term Effects of CPAP
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of CPAP therapy on various health outcomes, including cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and overall quality of life. Studies are investigating the role of CPAP in preventing or mitigating the progression of associated health conditions. This research is critical to establishing the long-term benefits and safety profile of CPAP therapy.
The focus is now on understanding the mechanisms underlying the benefits of CPAP and identifying subgroups of patients who may experience greater or lesser benefits. This ongoing research will refine CPAP therapy, leading to improvements in patient outcomes.