Qual tipo de apneia do sono geralmente causa roncos altos?
Jul 13, 2025 / zsfcdn103/
Understanding Central Sleep Apnea
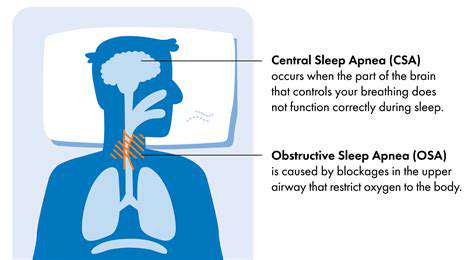
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, but unlike obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), these pauses aren't caused by a physical blockage of the airway. Instead, the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. This can lead to periods of shallow or no breathing, disrupting the natural sleep cycle and causing significant daytime sleepiness and fatigue. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of CSA is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This often involves comprehensive sleep studies to accurately identify the specific type and severity of the condition.
Causes of Central Sleep Apnea
Several factors can contribute to the development of central sleep apnea. These include certain medical conditions such as heart failure, stroke, and some neurological disorders. It's important to note that these conditions can exacerbate the underlying issues that lead to CSA, so the root cause must be addressed for effective treatment. Additionally, some medications, including those used to treat high blood pressure, can also be a contributing factor. Proper medical evaluation is essential for determining the specific cause in each case.
Symptoms of Central Sleep Apnea
Common symptoms of central sleep apnea may include excessive daytime sleepiness, headaches, difficulty concentrating, and morning confusion. These symptoms can significantly impact a person's daily life, reducing productivity and overall quality of life. Recognizing these symptoms is the first step towards seeking appropriate medical attention and diagnosis. Other symptoms might include loud snoring (although not as common as in obstructive sleep apnea), gasping or choking sensations during sleep, and frequent awakenings.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosis of central sleep apnea typically involves a comprehensive sleep study, often conducted in a sleep laboratory. This study monitors breathing patterns, heart rate, and brain activity during sleep. The results of these tests help determine if central sleep apnea is present and provide crucial insights into the severity of the condition. A thorough medical history and physical examination are also important components of the diagnostic process.
Treatment Options for Central Sleep Apnea
Treatment for central sleep apnea focuses on addressing the underlying medical condition, if applicable. This might involve adjusting medications, managing chronic conditions, or implementing lifestyle modifications to improve overall health. Medications and devices can also be prescribed to help regulate breathing patterns during sleep. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, while most commonly associated with obstructive sleep apnea, may also be beneficial in certain cases of central sleep apnea. The specific treatment approach will be tailored to the individual needs and circumstances of each patient.

Other Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders and Snoring

Other Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders
Sleep-related breathing disorders encompass a range of conditions that disrupt normal breathing patterns during sleep. These disorders can significantly impact an individual's health and well-being, affecting not only sleep quality but also daytime functioning. Understanding these disorders is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment, potentially preventing long-term complications.
Common types include obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea, and sleep-related hypoventilation. Each disorder presents unique characteristics and requires tailored approaches to diagnosis and management. Proper evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential to determine the specific cause and severity of the breathing issues.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses, or apneas, are typically caused by a blockage of the airway, often in the throat or nasal passages. During these episodes, the brain momentarily fails to receive the oxygen it needs, leading to a disruption in sleep patterns and potentially serious health implications.
Symptoms can range from snoring to daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can significantly impact a person's ability to perform daily tasks and maintain overall health, highlighting the importance of early intervention.
Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea (CSA) differs from OSA in that the breathing disruptions stem from a problem with the brain's signals to the respiratory muscles. In other words, the brain fails to send the proper signals to initiate or maintain breathing. This can result in periods of no breathing or very shallow breathing during sleep.
Recognizing the symptoms of CSA is vital for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Symptoms might include excessive daytime sleepiness, headaches, and difficulty concentrating. Early intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Sleep-Related Hypoventilation
Sleep-related hypoventilation is a condition in which the body doesn't breathe deeply enough during sleep. This can result from problems with the respiratory muscles or the brain's control of breathing. It often leads to low blood oxygen levels, which can have serious health consequences.
Consequences of Untreated Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders
Untreated sleep-related breathing disorders can have serious consequences for overall health. These conditions can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These long-term health risks highlight the importance of seeking medical attention for any suspected sleep-related breathing problems.
Furthermore, the impact extends beyond physical health, significantly affecting mental well-being, cognitive function, and overall quality of life. Addressing these disorders through appropriate medical management is crucial for mitigating potential long-term health complications.