今日利用可能な包括的な睡眠障害治療オプション
Jun 02, 2025 / zsfcdn103/
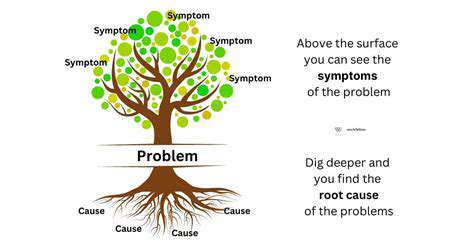
Understanding the Problem's Core
Pinpointing the fundamental origin of an issue remains vital for crafting lasting solutions. Surface-level fixes often prove inadequate; only by excavating deeper layers can we achieve meaningful progress. This exploratory phase typically demands meticulous scrutiny of all contextual elements, examining how various components interact to create the observed challenge.
Historical patterns and present conditions both require careful evaluation through data collection, stakeholder interviews, and document review. We're not simply hunting for a triggering event, but mapping the entire ecosystem of contributing influences that allowed the problem to emerge and persist.
Analyzing Contributing Factors
After initial problem identification, we must examine the constellation of elements that enable its occurrence. These might include organizational processes, individual behaviors, or environmental conditions. Comprehensive factor analysis separates effective solutions from temporary bandaids, ensuring we address the complete picture rather than isolated symptoms.
Understanding how these elements interact reveals the problem's true complexity. Pattern recognition and causal mapping create a three-dimensional view that prevents critical connections from being overlooked during the diagnostic process.
Developing a Framework for Investigation
Systematic problem-solving demands a structured investigative approach. This framework should specify data requirements, analysis methodologies, and evaluation criteria. A disciplined process guards against confirmation bias while ensuring thorough coverage of all potential causal pathways.
The framework must include mechanisms for validating hypotheses and challenging assumptions. This intellectual rigor prevents premature conclusions and maintains objectivity throughout the diagnostic journey.
Implementing Solutions & Monitoring Outcomes
Solution development should directly target the identified causal factors. Effective interventions require customization rather than generic applications, with careful consideration of how changes will interact with existing systems.
Continuous monitoring transforms implementation from an event into an evolutionary process. Tracking both intended outcomes and unintended consequences creates opportunities for refinement. This adaptive approach recognizes that complex systems rarely respond predictably to intervention, demanding flexibility in our improvement strategies.
Pharmacological Interventions: Medications for Sleep Disorders

Pharmacological Approaches to Managing Pain
Modern medicine offers diverse chemical tools for pain management across the intensity spectrum. These agents target specific neurological pathways, interrupting pain signals before they reach conscious awareness. Optimal outcomes typically emerge from combining pharmacological and behavioral strategies, creating multidimensional treatment plans.
Analgesic categories each possess distinct mechanisms and risk profiles. NSAIDs combat inflammation, opioids modulate central perception, while adjuvants address secondary pain components. Understanding these differences proves crucial for safe, effective prescribing.
Opioid Analgesics: A Complex Consideration
These powerful agents remain essential for severe pain despite their controversial profile. Their neurological action provides unmatched relief but demands vigilant oversight. Responsible use requires balancing therapeutic benefits against dependency risks through careful patient selection and monitoring protocols.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
These workhorse medications address both pain and inflammation through prostaglandin modulation. While generally safer than opioids, they still require consideration of individual risk factors, particularly regarding gastrointestinal and cardiovascular health. Their dual-action mechanism makes them first-line options for many inflammatory conditions.
Adjuvant Analgesics: Supporting Pain Management
Originally developed for other indications, these medications demonstrate surprising analgesic properties, particularly for neuropathic pain. Their value often lies in synergistic combinations, allowing reduced doses of primary analgesics while maintaining therapeutic effects.
Local Anesthetics: Targeted Pain Relief
These precision tools provide confined pain blockade without systemic effects. Modern formulations and delivery systems continue expanding their applications. Regional techniques now offer extended relief with minimal side effect profiles, revolutionizing perioperative pain management.
Individualized Pain Management: Tailoring Interventions
Effective treatment requires customization beyond diagnostic categories. Genetic factors, comorbidities, and personal preferences all influence medication selection and dosing. This personalized approach maximizes efficacy while minimizing adverse effects, creating truly patient-centered care.
Treatment plans should evolve with patient response, avoiding rigid protocols in favor of dynamic adjustment. This flexibility acknowledges pain's subjective nature and variable treatment responses among individuals.
Monitoring and Potential Side Effects: Important Considerations
Vigilant oversight remains critical throughout pharmacological treatment. Beyond pain metrics, we must track functional improvement and quality-of-life measures. Comprehensive monitoring catches subtle adverse effects before they escalate, particularly important with medications carrying abuse potential.
Medication reconciliation prevents dangerous interactions, especially for patients managing multiple conditions. Collaborative care models that include pharmacists enhance medication safety across treatment continuums.
Advanced Treatment Options: Emerging Technologies and Therapies

Advanced Surgical Interventions
Contemporary surgical innovations minimize tissue disruption while maximizing precision. Robotic systems enhance human capabilities, allowing maneuvers impossible with traditional techniques. These advancements dramatically reduce convalescence periods while improving surgical outcomes, particularly valuable in trauma scenarios where speed and accuracy prove critical.
Specialized instrumentation like advanced hemostatic devices and tissue-sealing technologies have transformed operative workflows. Such tools provide unprecedented control in hemorrhage management, significantly improving survival rates in emergency settings.
Pharmacological Enhancements
Next-generation pharmaceuticals target molecular pathways with increasing specificity. This precision reduces collateral damage to healthy systems while enhancing therapeutic effects. Modern drug development leverages deep biological understanding to create smarter interventions, moving beyond symptom management toward causal treatment.
Innovative formulations address previously untreatable conditions while improving safety profiles. Targeted delivery systems now maximize drug concentration at disease sites while minimizing systemic exposure.
Advanced Diagnostics and Monitoring
Cutting-edge imaging and biomarker analysis enable earlier, more accurate diagnoses. Portable technologies bring laboratory-grade testing to point-of-care settings. Rapid diagnostic capability transforms treatment timelines, particularly in time-sensitive conditions where delays prove catastrophic.
Continuous monitoring systems detect subtle physiological changes before clinical symptoms emerge. This anticipatory approach enables proactive intervention, preventing complications rather than reacting to them.
Specialized Critical Care Units
Dedicated environments concentrate expertise and technology for optimal outcomes. These units integrate advanced life support with specialized monitoring capabilities. Such focused resources prove invaluable for managing complex, unstable conditions requiring immediate, coordinated responses.
Protocolized care in these settings ensures consistency while allowing for individualization. The combination of specialized equipment and trained personnel creates an environment where critically ill patients receive optimal support.
Emerging Technologies in Emergency Medicine
Artificial intelligence applications analyze vast datasets to identify subtle patterns. Machine learning algorithms continuously improve their predictive capabilities. These tools augment clinical decision-making without replacing human judgment, particularly valuable in high-stakes, time-pressured scenarios.
Telehealth platforms dissolve geographical barriers to specialist care. Remote consultation capabilities ensure expertise reaches where it's needed most, democratizing access to advanced medical knowledge regardless of location.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies: Holistic Approaches
Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine
This ancient healing system views health through an energetic lens. Needle stimulation purportedly rebalances subtle energy flows. While Western science continues investigating mechanisms, many patients report subjective benefits, particularly for stress-related conditions that impact sleep quality. The holistic TCM paradigm considers lifestyle factors equally important as specific treatments.
Traditional diagnostics assess tongue appearance, pulse qualities, and constitutional patterns. Treatment plans often combine acupuncture with herbal formulations and dietary recommendations, creating multifaceted interventions.
Herbal Remedies for Sleep
Botanical preparations have accompanied human civilization for millennia. Modern research validates some traditional uses while challenging others. Quality control remains paramount, as potency varies significantly among sources. Professional guidance helps navigate potential herb-drug interactions, ensuring safe integration with conventional treatments.
Individual biochemistry influences herb effectiveness, making standardized dosing challenging. Careful titration and monitoring help identify optimal regimens while minimizing adverse effects.
Mindfulness and Meditation Practices
These attention-training techniques cultivate present-moment awareness. Regular practice appears to modulate stress response systems, creating physiological changes conducive to relaxation. Evidence suggests measurable impacts on sleep architecture, particularly for individuals with stress-related insomnia.
Various traditions offer different approaches, from focused attention to open monitoring techniques. Finding a compatible practice style enhances adherence and therapeutic benefits.
Yoga and Stretching for Better Sleep
Gentle movement practices prepare body and mind for rest. Specific sequences target tension accumulation patterns common in sedentary lifestyles. The combination of physical release and mental focus creates ideal pre-sleep conditions, particularly when practiced consistently.
Restorative yoga variations emphasize supported poses and prolonged relaxation. These approaches prove particularly valuable for individuals with chronic pain or hyperarousal states that interfere with sleep onset.