Jan 10, 2026 / zsfcdn103/
1. Understanding Micromanagement and Its Impact
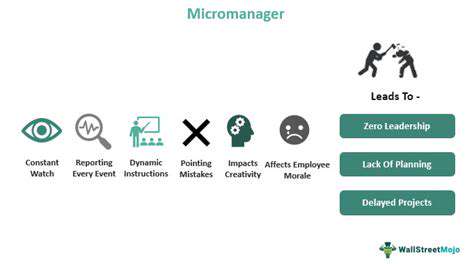
Micromanagement refers to a management style where a manager closely observes or controls the work of their employees. This approach can severely hinder productivity and employee morale. Research from Gallup indicates that under micromanagement, employee engagement drops significantly, often leading to higher turnover rates.
When employees feel they are not trusted or valued, their motivation declines. Many professionals have expressed that consistent micromanagement makes them feel powerless and undervalued. It is crucial for managers to recognize these subtle cues to promote a healthier working environment.
2. The Psychological Effects of Micromanagement
- Creates a culture of fear and anxiety.
- Leads to decreased job satisfaction.
- Reduces innovative thinking and creativity.
The psychological toll of micromanagement can be profound. Workers in such environments often experience heightened stress levels, which can lead to burnout over time. This is not only detrimental to employees but can also impact the company's bottom line. Moreover, an oppressive atmosphere stifles innovation, preventing employees from bringing new ideas to the table.
3. Identifying Micromanagement in Your Style
One way to evaluate if you’re micromanaging is by reflecting on your interactions with team members. Do you frequently check in or require constant updates on their work? These behaviors can indicate a lack of trust that erodes team dynamics. Recognizing this pattern is the first step toward adjusting management style.
Another sign is the reluctance of employees to share their concerns. If they seem hesitant or guarded when discussing their tasks, it might be a result of past micromanagement experiences. Encouraging open communication can help mitigate these feelings.
4. Strategies to Combat Micromanagement
- Encourage autonomy.
- Set clear expectations.
- Provide support without hovering.
To shift away from micromanagement, leaders should focus on empowering employees. One effective strategy is to establish clear goals and expectations, allowing team members the freedom to execute tasks in their way. This not only enhances productivity but also boosts Employee satisfaction and creativity. By stepping back, managers can focus on providing guidance and feedback instead of dictating every detail.
5. The Long-Term Benefits of Reducing Micromanagement
Reducing micromanagement has significant long-term benefits for a team and organizational culture. Employees who feel trusted are more likely to take initiative and develop leadership qualities. Furthermore, this fosters a culture of accountability and responsibility across the entire team.
Long-term repercussions include lower employee turnover and a more engaged workforce. Companies that adopt a hands-off approach often see improved overall performance metrics. By investing in trust and autonomy, managers can ultimately enhance both employee satisfaction and organizational success.
2. Poor Time Management Practices
Understanding Time Management Failures
Time management failures are a common issue facing managers today, impacting not only their productivity but also their team's efficiency. According to a report from the American Psychological Association, over 60% of employees feel overwhelmed by their workload. This indicates a broader pattern of poor time allocation, which can be traced back to ineffective prioritization of tasks. When managers fail to distinguish between urgent and important tasks, they often find themselves in a reactive mode rather than a proactive one.
Managers may also misallocate time by falling victim to multitasking, believing they can juggle multiple projects successfully. However, research from Stanford University reveals that multitasking can reduce productivity by as much as 40%. Thus, focusing on one task at a time not only enhances output quality but also leads to a more organized approach toward time management.
Strategies to Enhance Time Management
One effective strategy for improving time management is the adoption of the Eisenhower Matrix, which helps prioritize tasks by urgency and importance. By classifying tasks into four categories—urgent and important, important but not urgent, urgent but not important, and neither urgent nor important—managers can allocate their time more effectively. Implementing this framework encourages thoughtful planning and facilitates better decision-making in a time-saturated work environment.
Additionally, time blocking can serve as a concrete method to manage a manager's schedule. By allocating specific time periods for particular tasks, such as meetings, strategic planning, or project work, managers can minimize distractions and enhance focus on the task at hand. This intentional structuring of the workday often leads to a more streamlined approach to achieving daily goals and objectives.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While it’s crucial to implement Effective time management techniques, there are pitfalls managers must be cautious of. One major misstep is failing to set realistic deadlines. Underestimating the time required for a project not only causes stress but also affects team morale when deadlines are persistently unmet. A survey conducted by Gallup found that 80% of employees are more productive when they feel their managers set achievable goals and timelines.
Another common pitfall is neglecting regular check-ins and feedback sessions. Managers who overlook the importance of ongoing assessments leave room for miscommunication and misalignment within their teams. Establishing a culture of regular feedback can keep the team on the same page and encourage a sense of accountability, which, in turn, promotes better time management practices overall.
3. Failing to Set Clear Goals

Defining Clear Objectives
Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals is essential for effective management. Without clear objectives, teams often lack direction, leading to wasted resources and diminished morale. Managers should prioritize the creation of clear objectives that align with organizational goals.
A recent study by the Dominican University of California indicated that people who wrote down their goals were 42% more likely to achieve them. This statistic underscores the importance of documenting goals and closely tracking progress to ensure accountability.
Communicating Goals Effectively
Even the most well-defined goals can fall flat if they aren’t communicated effectively across the team. It’s important for managers to not only announce goals but also engage team members in discussions about how they can contribute. Clarifying roles ensures that everyone understands their responsibilities, significantly enhancing the chances of successful goal achievement.
Aligning Individual and Team Goals
When individual aspirations don't align with team objectives, it can create friction and hinder productivity. Managers should actively facilitate conversations between team members to ensure personal goals complement team and organizational goals. This alignment fosters a culture of collaboration and shared purpose.
Regularly Reviewing Progress
Tracking progress is crucial for maintaining focus and momentum. Regular check-ins can help identify obstacles and provide opportunities for feedback. Incorporating these evaluations into team routines not only keeps individuals accountable but also allows for adjustments to be made in real-time, optimizing performance.
Research suggests that teams that hold regular review sessions are 30% more likely to meet their targets compared to those who don’t. This statistic highlights the need for consistent interaction around goal progress.
Adjusting Goals as Necessary
Flexibility is key in goal-setting. Managers must be open to modifying objectives if circumstances change or if they find that certain goals are no longer relevant. By being adaptive, teams can respond to new challenges without feeling defeated. It's essential to convey to team members that flexibility does not equate to failure.
Encouraging a Goal-oriented Culture
Establishing a culture that values goal-setting can significantly improve overall team morale and productivity. Managers should celebrate achievements and encourage team members to share their goals with others. This fosters an environment of support and motivates everyone to strive for collective success.
Organizations that prioritize a goal-oriented culture report higher employee satisfaction rates. This demonstrates that a focus on shared objectives can lead to stronger team cohesion and greater individual commitment.
4. Neglecting Employee Feedback
Understanding the Importance of Employee Feedback
Employee feedback plays a crucial role in shaping company culture and driving organizational success. Frequent feedback not only aids in personal development but also aligns individual objectives with the company’s overall goals. According to a Gallup study, organizations that prioritize regular feedback see a 14% increase in productivity, highlighting how impactful this simple act can be.
Moreover, acknowledging employee feedback fosters an environment of trust and respect. When employees feel their voices are heard, they are more likely to engage in their work and contribute constructively. This trust translates into higher retention rates and lower turnover costs, ultimately benefiting the organization financially and culturally.
Common Pitfalls in Collecting Feedback
Managers often make the mistake of collecting feedback in a one-size-fits-all manner, failing to tailor their approach to the individual needs of their teams. For instance, using generic surveys may not yield actionable insights since these tools may not capture the nuances of each employee's experience. Implementing diverse feedback methods, such as one-on-one conversations or anonymous suggestion boxes, allows for a richer, more honest array of responses.
Additionally, neglecting to follow up on feedback can be a severe misstep. When employees do not see any changes implemented based on their comments, they may feel discouraged and less likely to share insights in the future. Creating a structured response plan for addressing feedback not only shows employees that their opinions matter but also encourages continuous improvement within the workplace.
Creating a Feedback-Driven Culture
To cultivate a Feedback-driven culture, managers must actively encourage open discussions and establish regular feedback channels. This can include setting up monthly check-ins, casual coffee chats, or structured performance reviews that emphasize two-way communication. By normalizing feedback, organizations create an atmosphere where employees feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and recommendations.
Training managers to effectively solicit and respond to feedback is equally important. They should learn techniques for asking open-ended questions and demonstrating genuine interest in employee perspectives. Workshops that focus on communication skills can address vital areas, such as active listening and empathetic responses, leading to more engaging and fruitful discussions.
5. Lack of Work-Life Balance Awareness
Understanding Work-Life Balance
Work-life balance is not just a buzzword thrown around in corporate circles; it is a critical component of employee satisfaction and productivity. According to a 2019 survey by FlexJobs, 73% of professionals cited work-life balance as one of the most important factors in their job satisfaction. When organizations underestimate the importance of this balance, they may inadvertently foster environments where burnout is more likely to occur.
Moreover, a study by the Harvard Business Review highlighted that employees who perceive a better work-life balance are 21% more productive. This indicates that a focus on well-being can lead directly to more significant output, making awareness and action on this front not just an employee concern, but a business imperative.
Consequences of Ignoring Balance
Failing to promote a work-life balance can have dire consequences for both employees and the organization itself. Notably, high-stress levels can lead to elevated employee turnover rates; a report from Gallup suggests that organizations that ignore their employees' work-life balance often see a turnover rate 18% higher than those that prioritize it. This not only affects team dynamics but can also be a costly affair for recruitment and training of new staff.
In addition, poor work-life balance contributes to increased absenteeism. According to a study from the American Psychological Association, organizations with a culture that neglects employee wellness experience 37% higher rates of absenteeism. This directly impacts productivity as projects may face delays and workload shifts, stressing other team members.
Strategies for Managers
To enhance work-life balance awareness, managers should lead by example. This means demonstrating a commitment to balance in their own schedules and encouraging employees to take their full allotted time off. Implementing flexible working hours also allows employees to manage personal responsibilities more effectively while meeting their professional obligations.
Additionally, promoting open communication around workloads can help identify issues before they become major stressors. Regular check-ins and performance reviews can provide opportunities for employees to voice their concerns about workload and balance issues, providing managers with the necessary insights to make adjustments.
Tools and Practices to Support Balance
Utilizing technology can also greatly facilitate better work-life balance. Tools such as project management software and communication platforms can enhance efficiency by keeping everyone informed and aligned without the need for excessive meetings. Furthermore, these tools can help employees set their own schedules, allowing them to work during their most productive hours without sacrificing personal commitments.
Mindfulness and wellness programs are other effective avenues businesses can explore to support their employees' well-being. Implementing initiatives such as stress management workshops can equip employees with tools to cope with stress better, leading to improved workplace morale and performance.
Assessing Organizational Culture
Work-life balance is a reflection of an organization's culture, and it is essential for leadership to regularly assess how well their current practices align with promoting a supportive environment. Employee feedback surveys can be incredibly insightful for gauging how staff members feel about their workloads and the balance they are able to maintain. Through these assessments, managers can identify gaps in policies and practices that may not support employee well-being effectively.
It is critical for managers to remember that work-life balance is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different employees have different needs and responsibilities outside of work. Acknowledging this diversity and creating a more inclusive plan that meets the varied requirements of team members can lead to a more engaged, resilient workforce that ultimately drives better results for the organization.